Most people recognize the benefits of having portable generators for backup or recreational use but some will certainly overlook that these things can actually be dangerous. As a matter of fact, careless use of these handy machines can result in serious injury or even death. A 2007 ruling from the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (http://www.cpsc.gov) reported that nearly 100 documented deaths from 2005 to 2006 caused by carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning. Carbon monoxide is a by-product of the fuel combustion that happens inside the engines of power generators. It is a highly toxic gas that is colorless and odorless which make it extremely hazardous. It is said to kill in minutes.
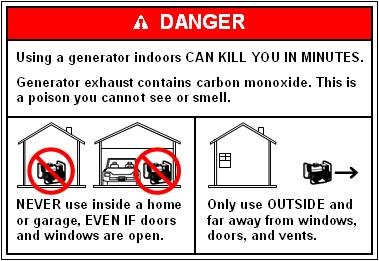
Other types of danger that users need to watch out for are those that pertains to shock or electrocution hazards, fire hazards and nose/vibration hazards. Enumerated below are some tips on how to mitigate these risks/dangers:
- Never install or use a generator within the confines of your home; not even in the garage with the garage door or windows open. Run a generator only outside the house (e.g. Outdoors).
- When installed outdoors, make sure it is not near any doors, windows, vents, especially if there’s a strong possibility that fumes or emissions can go inside them and cause a buildup inside the house.
- Wherever you put the generator to run, make sure the area is well ventilated. The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (http://www.osha.gov) recommends that you give the unit 3 to 4 feet of clear space on all sides and above it (e.g. inside a shed) to allow for proper air ventilation.
- Be wary of the symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning: dizziness, headaches, fatigue, nausea, etc. If you start getting the symptoms, run outside for fresh air and seek medical help immediately.
- Never connect a generator directly to your home’s circuits without professional help. A faulty connection can cause electrocution, injury, death and/or damage to property.
- Plug electrical devices or appliances directly to the generator using suitable cords. Check the cords for damage use only those that match the load rating of the appliances. Using an underrated cord can cause fire.
- Avoid using a generator in a wet or damp setting especially if it is not equipped for use in such.
- Make sure that the generator is properly grounded and do not operate a unit that has been wet or submerged in water without having it looked at first by a professional.
- Avoid spilling fuel on any part of the generator especially those that go hot during operation.
- Make sure you take necessary steps to prevent spills during refueling. Use only approved refueling or storage containers that are clearly marked as so.
- Store fuel storage tanks near living areas. Make sure they don’t go near objects that produce flame or heat. Fumes escaping from storage areas can ignite.
- Shut off and allow a generator to cool down before refueling.
- Install and operate generators away from work and living areas as the noise can cause hearing loss.
Sources:
http://www.cpsc.gov/cpscpub/prerel/prhtml07/07074.html
http://www.cpsc.gov/businfo/frnotices/fr07/pganpr.pdf
http://www.osha.gov/OshDoc/data_Hurricane_Facts/portable_generator_safety.pdf
http://www.nsc.org/news_resources/Resources/Documents/Portable_Generator_Safety_Tips.pdf